Cucumber, scientifically known as Cucumis sativus, is a widely cultivated annual plant belonging to the Cucurbitaceae family. The plant is known for its creeping vine and cylindrical to spherical fruits, which are consumed in various ways, such as pickled or as part of salads. Often, people wonder if cucumbers are considered fruits or vegetables, as they are typically used in savory dishes.

Botanically, cucumbers are classified as fruits because they grow from a single flower with only one ovum and contain seeds inside. This may come as a surprise to some, as cucumbers are commonly perceived as vegetables in the culinary world due to their usage in salads and savory recipes. In fact, they are even considered part of the daily recommended vegetable intake.
To sum it up, cucumbers hold a dual identity as both fruits and vegetables: botanically a fruit, but culinarily a vegetable. This intriguing classification invites further exploration and underscores the fascinating diversity found within the world of fruits and vegetables.
Cucumber Classification
Cucumbers are an interesting food item that often sparks curiosity regarding their classification. In the world of science and botanical definitions, cucumbers are considered a fruit. This is because they develop from the flower of the cucumber plant and contain seeds needed for reproduction 1. The scientific classification of cucumbers comes down to their origin from the plant’s ovary, like all other fruits.
However, in culinary practices, cucumbers are often treated as vegetables. This classification stems from their usage in various dishes and their relatively low sugar content compared to typical fruits. As a result, cucumbers find their place in main courses and side dishes, rather than sweet desserts.
Cucumbers belong to the gourd family and are a type of pepo2. A pepo is a type of fruit with a tough outer rind and fleshy center, which includes other members such as watermelon and pumpkins. Therefore, while cucumbers share some characteristics with vegetables, their scientific categorization as a fruit still holds true.
It is also worth noting that there is another group of fruits known as berries. However, cucumbers do not fit into the berry classification, as berries have a softer outer layer and contain seeds inside a soft, fleshy interior. Examples of true berries include grapes and blueberries. So, in conclusion, cucumbers are primarily classified as fruits from a botanical perspective, while their culinary treatment often places them alongside vegetables.

Different Varieties of Cucumbers
Cucumbers come in a variety of types, mainly categorized into slicing cucumbers and pickling cucumbers. Each variety is best suited for different uses in the kitchen, giving you plenty of options for incorporating this versatile fruit into your dishes.
Slicing cucumbers are typically larger in size and are best enjoyed fresh, uncooked in salads, sandwiches, or as a healthy snack. They usually have thick, dark green skin and fewer seeds. Some popular slicing cucumber varieties include:
- English Cucumber: Known for their thin skin, mild flavor, and elongated body, these cucumbers are seedless and don’t need to be peeled before consumption.
- Armenian Cucumber: These cucumbers are long, thin, and slightly variegated in shades of light green. They have soft seeds and thin skin, making them perfect for eating raw without any seeding or peeling.
- Chinese Snake Cucumber: Also known as Serpent Cucumbers, these can grow up to 2 feet in length and offer a sweet, juicy flesh that is perfect for salads and sandwiches. Their thin, delicate skin doesn’t require peeling, and they are commonly used in Chinese cuisine.
Pickling cucumbers, on the other hand, are smaller and have thicker, bumpier skin that can withstand the pickling process. Their size and shape allow them to fit nicely into jars for fermenting or storing in a vinegar brine. Some notable pickling cucumber varieties include:
- Gherkin: Gherkins are small, bumpy-skinned cucumbers often used for making pickles. They have a crisp texture, making them ideal for pickling whole.
- Kirby Cucumber: This variety is known for its irregular shape, bumpy skin, and crunchiness. They are ideal for making dill pickles and can also be enjoyed fresh in salads.
- Brown Russian Cucumber: Originating from Ukraine, this unique heirloom variety features brown-speckled skin and a plump body that reaches up to 3 inches wide. It’s perfect for pickling and can also be eaten fresh.
Each variety of cucumber offers its own unique flavor, texture, and appearance. No matter your preference or culinary needs, these versatile fruits can be used in a wide array of dishes to provide refreshing taste and endless possibilities. Choose a cucumber that best fits your needs, whether for slicing or pickling, and experience the many delicious offerings of this abundant produce.

Cucumber in the Culinary World
Cucumbers are a versatile ingredient used across numerous cuisines around the world. They provide a refreshing and mildly flavored ingredient, making them a popular choice for incorporating into various dishes. From a culinary perspective, cucumbers are generally treated as vegetables despite being botanically classified as fruits.
In the culinary world, chefs often utilize cucumbers in a variety of salads and savory dishes. Cucumbers are commonly found in green salads, offering a satisfying crunch and refreshing taste. They can also be paired with other ingredients to create more distinctive salads, such as those featuring a blend of tomatoes, olives, onions, and feta cheese.
In addition to salads, cucumbers can be found in several different types of dishes. They are sometimes incorporated into soups, either chilled or warm, providing a pleasant contrast in texture and flavor. Cucumbers can also be used in stir-fries, lending their distinctive crunch and subtle taste to the dish. Furthermore, sliced cucumbers are occasionally used as a topping in sandwiches, contributing a refreshing element to an otherwise simple meal.
Beyond these more traditional culinary uses, chefs continue to explore new ways to incorporate cucumbers into their creations. Cucumbers can lend their unique flavor profile to various dishes, allowing for experimentation and innovation in the culinary world. As a result, the cucumber’s role in the culinary world extends far beyond what one might initially expect, proving itself to be a truly versatile and valuable ingredient.
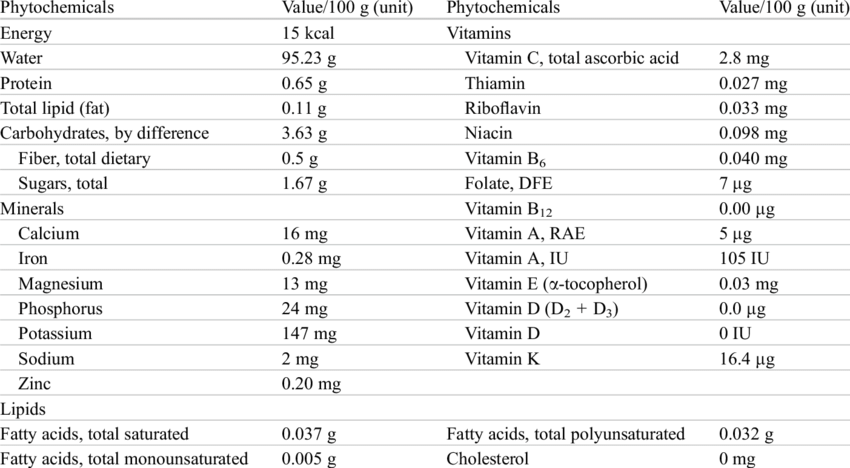
Nutritional Value of Cucumbers
Cucumbers are a nutritious and hydrating fruit, known for their low calorie content and refreshing taste. A half-cup of sliced cucumber (52g) with the peel contains only 8 calories, making it an ideal choice for those seeking a healthy snack or addition to a meal.
In terms of macronutrients, cucumbers have a minimal amount of fat and protein, with just 0.1g of fat and 0.3g of protein per half-cup serving. The majority of their energy comes from 1.9g of carbohydrates, which includes 0.3g of fiber and 0.9g of sugars.
Cucumbers offer a variety of essential vitamins and minerals. One of their standout features is their richness in vitamin K; a single serving provides 62% of the recommended daily intake (RDI). Vitamin K plays a crucial role in blood clotting and bone health. Additionally, cucumbers contain a good amount of vitamin C, contributing to 14% of the RDI, which supports a healthy immune system and collagen production.
Besides vitamins, cucumbers are a source of key minerals such as potassium and magnesium. A single serving boasts 13% of the RDI for potassium and 10% of the RDI for magnesium. Potassium helps maintain proper electrolyte balance and supports nerve function, while magnesium contributes to muscle and nerve function, as well as bone health.
Although cucumbers have a low sodium content at only 1mg per half-cup serving, they may be enjoyed as part of a balanced diet to fulfill nutritional needs and add a crisp, refreshing element to various dishes.

Health Benefits and Uses of Cucumber
Cucumbers are not only a refreshing and versatile ingredient in various dishes, but they also have several health benefits. Rich in water content, cucumbers provide excellent hydration for the body, making them ideal for consumption during hot weather or after physical activities.
Cucumbers are a good source of antioxidants, which help protect the body from cellular damage caused by free radicals. Antioxidants are known to reduce inflammation, support healthy aging, and boost overall health. Moreover, cucumbers possess anti-inflammatory properties, which can help reduce swelling and alleviate discomfort in various parts of the body.
Including cucumber in your diet can also improve digestion and prevent constipation. The high water content, along with a decent amount of dietary fiber, is beneficial in the digestive process, promoting regular bowel movements.
Another impressive feature of cucumbers is their potential to support weight loss. Due to their low-calorie content and high water composition, cucumbers can make you feel full, preventing overeating and aiding in weight management.
Cucumbers have multiple uses when it comes to skincare as well. The hydrating and soothing properties can be beneficial in creating face masks, providing relief from skin irritation, redness, and puffiness.
In conclusion, incorporating cucumbers into your regular diet and skincare routine can offer numerous health benefits, including hydration, improved digestion, weight management, and better skin health. Remember to consume the peel as well, as it contains a significant portion of the cucumber’s essential nutrients.

Cucumber in Relation to Other Fruits
Cucumbers share similarities with various fruits in the plant kingdom. They belong to the gourd or cucurbitaceae family, making them botanically related to other fruits like melons, squash, and pumpkins. Just like cucumbers, these fruits have seeds in the middle and grow from a flower, which technically classifies them as fruits according to botanists.
Tomatoes are another well-known fruit that is often mistaken for a vegetable. They, too, have seeds and grow from a flower, which puts them in the same botanical category as cucumbers. Both cucumber and tomato are members of distinctive botanical groupings; cucumbers belong to the cucurbitaceae family, while tomatoes are part of the solanaceae family.
Melons, such as watermelon and cantaloupe, are close relatives to cucumbers as they all belong to the same cucurbitaceae family. Despite their distinct taste and texture differences, these fruits share common growth patterns and characteristics with cucumbers.
Squash, including pumpkins and zucchini, shares a botanical connection with cucumbers as well. They all fall under the cucurbitaceae family, signifying a similar fruit composition. As a result, they have seeds inside and grow from a single flower with one ovum, making them botanically fruits like cucumbers.
On the other hand, fruits like lemons are not related to cucumbers in terms of botanical classification. Lemons are part of the citrus family, which is different from the cucurbitaceae family to which cucumbers belong.
In conclusion, cucumbers share close relations with various fruits such as melons, watermelons, squash, pumpkins, and zucchini. They all belong to the same cucurbitaceae family, making them botanically fruits. Other fruits like tomatoes are related but belong to different botanical families, while lemons are from an entirely separate category.

Biology and Growing Conditions of Cucumber
Cucumber (Cucumis sativus) is a widely cultivated plant belonging to the gourd family, Cucurbitaceae. This creeping vine plant produces cylindrical to spherical fruits that are consumed as vegetables. The roots of the cucumber plant grow in the ground, while the vines wrap around supporting frames or trellises using thin, spiraling tendrils.
Cucumbers are believed to have originated in the slopes of the Himalayas, but they are now cultivated worldwide. The plant bears yellow flowers that develop into the cucumber fruit. Pollination is necessary for typical cucumber varieties, as they require the transfer of pollen from male to female flowers. However, some newer cucumber varieties called parthenocarpic cucumbers are capable of producing fruits without pollination by developing seedless fruits.
The growing conditions required for cucumbers include well-drained soil and a consistent supply of water, as the roots tend to dry out easily. The plants thrive best at temperatures above 20 °C, making them suitable for cultivation in temperate zones [source]. Trellises or other supports are recommended for cucumber plants, as this helps keep the fruit off the ground, minimizing the risk of rot and disease.
There are various types of cucumbers, such as slicing, pickling, and seedless, each with their unique characteristics. One popular variety is the burpless cucumber, which is known for having a thinner skin and reduced bitterness compared to standard cucumbers, making them more pleasant to consume.
In summary, cucumber is a creeping vine plant from the gourd family, Cucurbitaceae, with cylindrical to spherical fruits widely used in culinary applications. The plant requires well-drained soil, a consistent water supply, and temperatures above 20 °C for optimal growth. Proper trellising and support can help improve fruit quality and reduce the risk of disease.

Cucumber in the Produce Aisle
Cucumbers are a common sight in the produce aisle of most grocery stores. They are usually found alongside other popular produce items such as tomatoes, lettuce, and bell peppers. These cylindrical green fruits are a favorite for many consumers due to their crisp texture and refreshing taste.
In the produce section, cucumbers are often available in two main types: slicing cucumbers and English cucumbers. Slicing cucumbers, the more common variety, feature a thicker, dark green skin and are typically shorter in length. English cucumbers, on the other hand, have thinner skin, a milder taste, and are often sold wrapped in plastic to help maintain freshness.
When shopping for cucumbers, it is important to examine their external appearance. A healthy cucumber should have a firm, smooth, and unblemished skin. Avoid picking ones with wrinkles, soft spots, or discoloration, as these signs may indicate that the fruit has started to go bad.
Cucumbers are versatile fruits that can be used in various dishes and recipes, both raw and cooked. They can be sliced and added to salads, sandwiches, and wraps, or be used as crunchy toppings for tacos, burgers, and other dishes. Cucumbers can also be pickled, a preservation method that adds unique flavor and extends shelf life.
Although not as nutrient-dense as some other produce items, cucumbers still offer health benefits. They are composed of roughly 96% water, making them an excellent choice for hydration and weight management. Additionally, they contain antioxidants that may help reduce inflammation.
Next time you find yourself in the produce aisle of a grocery store, don’t forget to consider adding this refreshing and versatile fruit to your shopping cart.

Frequently Asked Questions
What classifies a vegetable as a fruit?
A vegetable is classified as a fruit when it develops from the ovary of a flowering plant and contains seeds. Botanically speaking, fruits are categorized by their structure and organization within a plant. For example, cucumbers are considered fruits because they possess seeds and grow from the ovary of the plant.
How is a cucumber related to a berry?
Cucumbers are related to berries through their classification within the gourd or cucurbitaceae family of plants. Both are considered botanical fruits because they grow from the ovary of a flowering plant. However, their texture, shape, and taste significantly differ. Cucumbers are classified as pepo fruits, which have a hard outer rind and fleshy center, while berries are typically softer and contain a higher water content.
What connects pumpkins, squash, and cucumbers?
Pumpkins, squash, and cucumbers share a connection because they all belong to the gourd or cucurbitaceae family of plants. These plants have common features such as a sprawling growth habit, tendrils for climbing, and large flat seeds. Although they are popularly considered vegetables in culinary terms, botanically, they are all classified as fruits since they grow from the flowering part of the plant and contain seeds.
Why are tomatoes classified as fruits?
Tomatoes are classified as fruits due to their botanical characteristics. They develop from the ovary of a flowering plant and contain seeds, meeting the criteria for a fruit in botanical terms. Like cucumbers, tomatoes are often used as vegetables in culinary dishes, which leads to confusion regarding their classification.
How can you differentiate a fruit from a vegetable?
In botanical terms, fruits develop from the ovary of a flowering plant and usually contain seeds. Examples include apples, strawberries, and cucumbers. Vegetables, on the other hand, are the other parts of plants such as stems, leaves, and roots. Examples of vegetables include lettuce, spinach, and carrots. In culinary terms, fruits are typically sweet and used in desserts, while vegetables are savory and used in main dishes or side dishes.
Which common vegetables are actually fruits?
Several commonly recognized vegetables are, in fact, fruits from a botanical perspective. Some examples are avocados, bell peppers, cucumbers, pumpkins, squash, and tomatoes. These foods are considered fruits because they develop from the flowering part of the plant and contain seeds. However, due to their savory taste and usage in culinary dishes, they are often referred to as vegetables.
Footnotes
- (https://farmingthing.com/cucumber-fruit-vegetable-classification/) ↩
- (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cucumber) ↩
- Why is My Poop Black: Uncovering the Causes and Solutions - December 21, 2023
- Clear Protein Drinks: Optimal Hydration and Muscle Support for Athletes and Fitness Enthusiasts - December 21, 2023
- Does Apple Juice Make You Poop: Uncovering the Digestive Effects - November 29, 2023








